Understanding Transportation: Definition and Importance
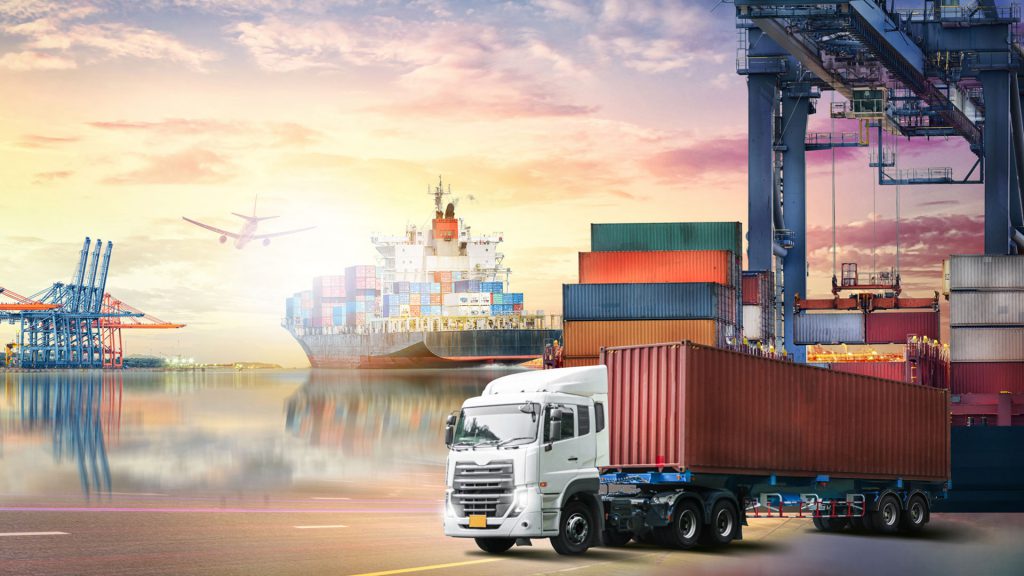
Transportation is a fundamental aspect of modern life that enables the movement of people and goods across various distances and locations. It is a vital service that connects communities, fosters economic development, and supports lifestyle conveniences. Within the realm of Transportation, various modes and systems serve distinct needs and demands, shaping how we navigate urban landscapes and interact socially and economically.
What is Transportation?
Transportation refers to the intentional movement of humans, goods, or animals from one place to another. It encompasses a diverse range of modes, including roads, railways, waterways, and airways. At its core, transportation is not just about mechanics; it is about creating networks that allow for efficient travel and exchange. The significance of transportation can be seen in public transit systems, freight services, and personal vehicles, each serving critical roles in our daily lives.
The Role of Transportation in Daily Life
Transportation plays an essential role in our everyday existence. It affects where we live, work, and socialize. Efficient transportation systems facilitate access to jobs, education, healthcare, and recreation. For instance, cities with robust public transit options often see higher rates of employment and better access to essential services. Conversely, inadequate transportation can lead to traffic congestion, diminished economic opportunities, and restricted access to essential services, making it a crucial area of urban planning and policy development.
Impact of Transportation on Urban Development
Urban development is significantly influenced by transportation systems. Well-planned infrastructure supports the growth of communities and attracts businesses. As cities expand, the effectiveness of their transportation networks can often determine the overall quality of life. For example, cities like Chicago and New York thrive due to their extensive public transport systems, which ease congestion and provide mobility for millions of residents and visitors. Sustainable transport solutions encourage more livable spaces, reduce pollution, and promote economic vitality.
Types of Transportation: A Comprehensive Overview
The transportation landscape is diverse, encompassing both public and private sectors. Understanding the various types of transportation available enables individuals and businesses to make informed choices tailored to their specific needs.
Public Transportation Options
Public transportation includes buses, trains, subways, ferries, and trams, providing affordable options for commuters. For instance, cities like San Francisco boast successful public transit networks through the Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) system, facilitating seamless travel across urban areas. Public transportation is environmentally sustainable and can greatly reduce traffic volumes, thereby minimizing the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
Private Transportation: Cars and Alternatives
While public transportation offers numerous benefits, private transportation remains prevalent, with personal vehicles often being the most convenient choice for many. The use of cars varies by region and individual preference. Alternatives such as car-sharing services, ridesharing applications like Uber and Lyft, and electric scooters have gained traction, providing innovative solutions to urban mobility challenges. These alternatives offer flexibility and often address the shortcomings of public systems, such as limited routes or schedules.
Emerging Technologies in Transportation
The transportation sector is undergoing a technological revolution, with advancements such as autonomous vehicles, smart traffic management systems, and electric transportation options revolutionizing the way we think about mobility. Technologies like self-driving cars have the potential to reduce traffic accidents and improve efficiency. Furthermore, innovations in battery technology and renewable energy sources are making electric vehicles more accessible and effective. Exploring these technologies can significantly enhance the integrity and reliability of transportation systems across the globe.
Choosing the Right Transportation Method for Your Needs
When selecting a transportation method, various factors should be considered to achieve an optimal balance between cost, convenience, and environmental impact.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Transportation
Choosing an appropriate transportation method requires weighing various factors such as distance, cost, travel time, and sustainability. For example, short trips may be best achieved through cycling or public transit, while longer journeys might necessitate a car, bus, or airline. Assessing personal circumstances, such as finances or family needs, also plays a vital role in making transportation choices.
Cost vs. Convenience: Finding the Balance
Cost and convenience often serve as competing factors in transportation decisions. While public transport may be more economical, it might also be less convenient due to limited schedules or routes. Conversely, private transportation grants flexibility but usually comes with added expenses, such as vehicle maintenance and fuel costs. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis helps individuals navigate these trade-offs more effectively.
Environmental Considerations in Transportation Choices
As concerns around climate change and sustainability grow, environmental impact has become a crucial consideration in transportation decisions. Opting for greener transportation methods, such as electric cars, public transportation, or cycling, can significantly reduce carbon emissions. Additionally, many cities are developing initiatives and incentives to encourage the use of eco-friendly transport options, making greener choices increasingly accessible to the public.
Evaluating Transportation Systems: Metrics and Performance
Proper evaluation of transportation systems is vital to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Implementing effective metrics enables stakeholders to make informed decisions that enhance service and infrastructure.
Key Performance Indicators for Transportation
Performance in transportation systems can be measured using various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as ridership levels, on-time performance, safety records, and cost efficiency. For instance, evaluating a public transit system’s ridership can help agencies determine effectiveness and areas requiring enhancement. Connecting this data to community needs and expectations informs better service delivery.
Case Studies: Successful Transportation Models
Real-world examples can illustrate effective transportation strategies. For instance, cities like Copenhagen have successfully integrated cycling into their transportation infrastructure, resulting in reduced traffic congestion and lower carbon emissions. Similarly, the extensive use of Mumbai’s suburban trains demonstrates how well-planned transit systems can cater to vast populations. Studying these models offers valuable insights for cities aiming to enhance their transportation capabilities.
Challenges in Transportation System Evaluation
Evaluating transportation systems does not come without challenges. Issues such as lack of data, political resistance, and funding limitations can impede efforts to assess effectiveness. Moreover, ensuring that evaluations factor in diverse community needs and changing demographics can prove tricky. Developing robust methodologies and collaborative approaches can help stakeholders surmount these challenges and foster well-functioning transportation networks.
Future Trends in Transportation: What to Expect
As we look forward, the landscape of transportation is set to evolve significantly. Staying ahead of emerging trends ensures cities and individuals can adapt to changing landscapes effectively.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Transportation
Innovative technologies are reshaping transportation, from the rise of autonomous vehicles to the integration of artificial intelligence in traffic management. Increased connectivity promises rapid advancements in infrastructure. Car-sharing and ride-hailing apps are changing car ownership paradigms, reflecting generational shifts in transportation preferences. Staying informed about these trends allows stakeholders to leverage advancements to enhance efficiency, accessibility, and sustainability.
Transportation Policy and Urban Planning
Transportation policies will play a crucial role in shaping future urban environments. Developing comprehensive strategies that prioritize public transport, promote eco-friendly alternatives, and integrate innovative technologies can greatly influence mass mobilization. Collaboration among governmental agencies, civil society, and private sectors is essential for policymaking aimed at establishing sustainable, accessible public transit networks.
Anticipating Changes in Consumer Behavior and Needs
Consumer behavior regarding transportation is shifting, particularly among younger generations who prioritize eco-friendly options and technological integration. Understanding these shifting preferences allows transportation providers and municipalities to plan accordingly, adapting services to meet evolving consumer desires. Engaging in community outreach and participative planning can facilitate the development of tailored solutions that embrace user-centric transportation models.